OEE Glossary
Quick Links
OEE Definitions
5 Why Analysis
5 Why Analysis is a simple process originally created by Sakichi Toyoda at the Toyota Motor Company for identifying the root cause behind a particular problem. Start with a problem definition, and keep asking “why” until the root cause is uncovered.
5S
5S is a Lean Manufacturing process that creates an organized work area. 5S has five steps:
- Sort: eliminate unneeded items
- Straighten: organize remaining items
- Shine: clean and inspect the work area
- Standardize: document standards for the area
- Sustain: apply and audit the standards
Actual Cycle Time
Actual Cycle Time is the actual time to produce one part. In OEE, it is calculated as Run Time divided by Total Count. It is used in calculating OEE Performance. A variation of the calculation uses Actual Run Rate instead.
Actual Run Rate
Actual Run Rate is the actual rate of production, when it is running. In OEE, calculated as Total Count divided by Run Time. It is used in calculating OEE Performance. A variation of the calculation uses Actual Cycle Time instead.
All Time
All time refers to every minute of every day — 24 hours in a day, 7 days in a week.
Andon
Andon is an indicator above production line to signal production conditions. It often uses green/yellow/red colors to indicate status.
Autonomous Maintenance
Autonomous Maintenance is a process from TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) for improving machine OEE by engaging operators to complete routine maintenance, inspection, and lubrication activities.
Availability Loss
Availability Loss is one of the three OEE Losses. Availability takes into account Equipment Failures and Setup and Adjustments. An Availability score of 100% means that the process is always running during Planned Production Time.
Best Practice
Best Practices are methods that are considered “state of the art” by the most respected in an industry. Successful production companies use different methods than unsuccessful companies.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a process for creating an expanded world of ideas and possibilities. Brainstorming is a divergent problem solving process that is intended to create a broad range of ideas that can then be refined by a root cause process.
Breakdowns
Breakdowns are a type of Unplanned Stop where time is lost due to Equipment Failure (one of the Six Big Losses). Breakdowns are a type of Unplanned Stop and affect OEE Availability.
Breaks
Breaks are considered unproductive time where the process is scheduled not to run because the crew is scheduled to be away from the line. Breaks are typically excluded from OEE calculations.
Capacity
Capacity is the maximum amount of production available if equipment is fully productive (running at 100% OEE), for All Time (24/7).
Changeover
Changeover means the manufacturing process is scheduled for production and is not running because of a planned Setup, Make Ready, or Adjustment event. Changeovers are a type of Planned Stop and affect OEE Availability.
Constraint
A constraint is the step of the manufacturing process that acts as a bottleneck to the throughput of the entire process. OEE should always be measured at the constraint as it is the slowest step in the process.
Countermeasures
Countermeasures are actions taken to counter or mitigate a manufacturing loss. A manufacturing loss may benefit from multiple countermeasures including immediate actions to prevent the loss from getting worse, short term fixes and long term root cause fixes.
Cycle Time
Cycle Time is the time to produce one part. It is the inverse of Run Rate.
Cycle Time Analysis
Cycle Time Analysis is a tool used to better understand issues that affect Performance. It is important to automate logging of Cycle Times for later analysis.
Defect
A defect is any part that is not right the first time. Defects may be reworked, or scrapped. All defects are a loss to OEE Quality.
Downtime
Downtime, also known as Stop Time, is all time where the manufacturing process was intended to be running but was not due to Unplanned Stops (e.g., breakdowns), or Planned Stops (e.g., changeovers).
Downtime Loss
Downtime Loss is production time lost to unplanned shutdowns. One of the three OEE Losses (reduces OEE Availability). Major focus area for improvement.
Equipment Failure
Equipment Failure means the manufacturing process is scheduled for production and is not running because of an unplanned event such as a machine break down. Equipment Failure is one of the Six Big Losses to OEE and affects OEE Availability.
Equipment Loss
Equipment Loss is the time when the plant is scheduled to run, but is not Fully Productive due to one of the Six Big Losses to OEE.
Error Proofing
Error Proofing is a process for improving OEE Quality by designing error detection and prevention into processes and equipment. The goal of error-proofing is to eliminate Process Defects and Reduced Yield.
First Pass Yield
First Pass Yield means making a Good Part, ‘right first time’ without rejecting it to be scrapped or reworked.
Focused Improvement
Focused Improvement is a highly effective process for reducing unplanned stop time. A small cross functional team selects a loss (often from a top loss report), and apply root cause analysis or 5 why analysis to identify potential causes and fixes. Focused Improvement is a technique from Lean Manufacturing and is sometimes known as a kaizen blitz.
Fully Productive Time
Fully Productive Time is the actual productive time after ALL losses are subtracted. An OEE score of 100% means that the process is Fully Productive with no Availability Loss, Performance Loss, or Quality Loss.
Good Parts
Good Parts are produced parts that meet quality standards (without rework). The quantity of Good Parts is referred to as Good Count which is used to calculate OEE Quality.
IDA (Information, Decision, Action)
IDA is one of the easiest and most effective ways to improve results by focusing on three factors that drive results (Information, Decisions, and Actions).
Ideal Cycle Time
Ideal Cycle Time, also known as Design Cycle Time, is the theoretical minimum time to produce one part. The inverse of Ideal Run Rate. Used to calculate OEE Performance. A variation of the calculation uses Ideal Run Rate instead.
Ideal Run Rate
Ideal Run Rate is the theoretical maximum production rate. The inverse of Ideal Cycle Time. Used to calculate OEE Performance. A variation of the calculation uses Ideal Cycle Time instead.
Idling and Minor Stops
Idling and Minor Stops means the manufacturing process is running, but is experiencing brief pauses in production that are not long enough to be tracked as Equipment Failures. This loss is often called Small Stops. Idling and Minor Stops is one of the Six Big Losses to OEE and affects OEE Performance.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing is a quality philosophy that strives to minimize consumption of resources that add no value to the finished product. OEE can be a key tool and metric in Lean Manufacturing programs.
Make Ready
Make Ready is a stage within a changeover process in which machine settings are fine-tuned before production (often based on the inspection of a first-off part). Make Ready events are a type of Planned Stop and affect OEE Availability.
Material Shortage
Material Shortage means the manufacturing process is scheduled for production and is not running because of an unplanned lack of materials. Material Shortages are a type of Unplanned Stop and affect OEE Availability.
Nameplate Capacity
Nameplate Capacity is the design capacity of a machine or process. It is used to determine Ideal Cycle Time or Ideal Run Rate.
Net Run Time
Net Run Time is the time remaining once Schedule Loss, Availability Loss, and Performance Loss are subtracted from All Time.
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)
OEE is the framework for measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of a process, by breaking it down into three constituent components (the OEE Factors). OEE helps you see and measure a problem so you can fix it, and provides a standardized method of benchmarking progress.
OEE Availability
One of the three OEE Factors. Takes into account Availability Loss (any events that stop planned production for an appreciable length of time). Must be measured in an OEE program, usually by recording the duration of Unplanned Stops and Planned Stops.
OEE Factors
OEE Factors are the three constituent elements of OEE (Availability, Performance, and Quality). Often it is more important to focus on the three OEE Factors than the consolidated OEE metric.
OEE Losses
OEE Losses are the three types of productivity loss associated with the three OEE Factors (Availability Loss, Performance Loss, and Quality Loss). The goal is to relentlessly work towards eliminating OEE Losses.
OEE Performance
OEE Performance is one of the three OEE Factors. It takes into account Performance Loss (factors that cause the process to operate at less than the maximum possible speed, when running). It must be measured in an OEE program, usually by comparing Actual Cycle Time (or Actual Run Rate) to Ideal Cycle Time (or Ideal Run Rate).
OEE Quality
OEE Quality is one of the three OEE Factors. It takes into account Quality Loss (parts which do not meet quality requirements). It must be measured in an OEE program, usually by tracking Reject Parts.
Performance Loss
Performance Loss is one of the three OEE Losses. Performance takes into account Idling and Minor Stops and Reduced Speed. A Performance score of 100% means when the process is running it is running as fast as possible.
Planned Production Time
Planned Production Time is the total time that equipment is expected to produce. It is calculated by subtracting Schedule Loss from All Time. Benchmark that OEE is measured against.
Planned Stop
Planned Stop means the manufacturing process is scheduled for production and is not running because of a planned event such as a changeover, setup, or make ready event. Planned Stop time is one of the Six Big Losses to OEE and affects OEE Availability.
Plant Shutdown
Plant Shutdown is the time when the factory has no plans to run production (typically because the factory is closed or has no shifts scheduled). Plant Shutdown is a Schedule Loss to TEEP. Plant Shutdown time is excluded from OEE calculations.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance is a process from TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) for improving OEE by carrying out maintenance activity based on either calendar time (replacing parts every few months) or loss data (replacing a part one week before it has historically failed).
Process Defects
Process Defects mean the manufacturing process is producing defective parts (also known as reject parts) during steady-state production. Often this loss is called Production Rejects. Process Defects are one of the Six Big Losses to OEE and affects OEE Quality.
Production Counts
Production Counts are parts produced during steady-state production.
Production Rejects
Production Rejects are rejected parts produced during steady-state production. It is also another term for Process Defects, and one of the Six Big Losses. It contributes to OEE Quality.
Quality Loss
Quality Loss is one of the three OEE Losses. Quality is a measure of First Pass Yield and takes into account Process Defects and Reduced Yield. A Quality score of 100% means when the process is running, it is only making good parts.
Reason Code
A Reason Code is an identification number or classification applied to an Event subcategory. It is used to tabulate statistics. Makes it much easier to get a handle on losses, especially downtime loss.
Reduced Speed
Reduced Speed means the manufacturing process is running, but is running slower than the Ideal Cycle Time. This loss is often called Speed Loss. Reduced Speed is one of the Six Big Losses to OEE and affects OEE Performance.
Reduced Yield
Reduced Yield means the manufacturing process is producing defective parts (also known as reject parts) during a period of time immediately after an Equipment Failure event or a Setup and Adjustment event. Often this loss is called Startup Rejects. Reduced Yield is one of the Six Big Losses to OEE and affects OEE Quality.
Reject Parts
Reject Parts are produced parts that do not meet quality standards right the first time. It is calculated by subtracting Good Parts from Total Parts. In the Six Big Losses, Reject Parts are either produced during steady-state production (Process Defects), or on startup after a stop event (Reduced Yield).
Rework Parts
Rework Parts are rejected parts that can be reworked and sold to the customer. Reworked parts do not affect the OEE calculation as they were not right first time. OEE does not make a distinction between parts that can be reworked and parts that are scrapped.
Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is a method of resolving a non-conformance, by tracing back from the end failure to its original (root) cause. The basic tool for understanding and eliminating the sources of productivity losses.
Run Rate
Run Rate is the production rate when actually producing (running). It is the inverse of Cycle Time.
Run Time
Run Time means the manufacturing process is scheduled for production and is running. Run Time is calculated by subtracting downtime from planned production time. Run time includes time when the process could be experiencing small stops, reduced speed, and making reject parts.
Schedule Loss
Schedule Loss is the time when the plant is not scheduled for production (e.g., plant shutdown, no orders, breaks and lunches). Schedule loss is excluded from OEE, and is a loss to TEEP.
Setup and Adjustments
Setup and Adjustments means the manufacturing process is scheduled for production and is not running because of a planned event such as a changeover or part change. This loss often includes Changeover, Make Ready events. Setup and Adjustments is one of the Six Big Losses to OEE and affects OEE Availability.
Shift Time
Shift Time is the period of time where a shift is scheduled to be running the machine.
SIC (Short Interval Control)
SIC is a factory-floor process for engaging operators and supervisors to maximize OEE by seeking quick improvement opportunities that they can implement in full during the shift. SIC (Short Interval Control) uses Six Big Loss data to enable teams to make ongoing course corrections during the shift.
Six Big Losses
Six Big Losses are the six categories of productivity losses that are almost universally experienced in manufacturing: Equipment Failure, Setup and Adjustments, Idling and Minor Stops, Reduced Speed, Process Defects, and Reduced Yield. Drill down into the three OEE Factors, and you will reach the Six Big Losses. Measure your process with OEE, and improve your process by addressing the Six Big Losses.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a systematic quality program that strives to limit defects to six standard deviations from the mean. One of the major focuses of Six Sigma is to reduce process variation. In most companies, Quality Loss will be by far the smallest of the OEE Losses. A Six Sigma or equivalent program may be necessary to maintain focus on quality improvements.
Slow Cycle
Slow Cycle is a cycle that took longer than the Ideal Cycle Time, but less than a Small Stop. Slow Cycles are a cause for Reduced Speed in the Six Big Losses. Contributes to OEE Performance.
Slow Cycle Threshold
Slow Cycle Threshold is a dividing point between a standard cycle, and one which is considered “slow” (a Slow Cycle). Setting a Slow Cycle Threshold can be used in Cycle Time Analysis to automatically identify slow cycles.
Small Stop
Small Stop is a brief pause in production, but not long enough to be tracked as Stop Time. An alternative term for Idling and Minor Stops in the Six Big Losses. Contributes to OEE Performance.
Small Stop Threshold
Small Stop Threshold is a dividing point between a Slow Cycle, and one which is considered a Small Stop. Setting a Small Stop Threshold can be used in Cycle Time Analysis to automatically identify Small Stop cycles.
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die)
SMED is a program for reducing setup time. Named after the goal of reducing setup times to under ten minutes (representing time with one digit). Often a part of programs to improve OEE Availability.
Speed Loss
Speed Loss is production time lost to equipment running below maximum rated speed. An alternative term for Reduced Speed in the Six Big Losses and affects OEE Performance.
Standardized Work
Standardized Work means documenting important machine operation and leadership activities to ensure that best practices are consistently captured and followed. It is extremely important that standardized work documents are treated as ‘living’ documents that are regularly updated as improvements are made.
Startup Rejects
Startup Rejects are rejected parts produced while equipment is adjusted for production. An alternative term for Reduced Yield in the Six Big Losses and contributes to OEE Quality.
Stop Time
Stop Time, also called Downtime, is all time where the manufacturing process was intended to be running but was not due to Unplanned Stops (e.g., breakdowns), or Planned Stops (e.g., changeovers).
Takt Time
Takt Time is the production rate needed to meet customer demand. It is where sales and business planning meets the factory floor.
TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance)
TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) is a performance metric for measuring the true capacity of your manufacturing operation. TEEP takes into account equipment losses (as measured by OEE) and schedule losses (as measured by Utilization). It is calculated by multiplying OEE % by Utilization %.
Theory of Constraints
Theory of Constraints is a methodology for improving productivity that was proposed by Eli Goldratt in his bestselling 1984 novel The Goal. Dr. Goldratt proposed that every complex system, including manufacturing processes, consists of multiple linked activities, one of which acts as a constraint upon the entire system (i.e., the constraint is the “weakest link in the chain”).
Top Losses
Top Losses create an easily understood pareto-style report for quickly identifying losses to OEE. A good Top Losses report includes all Six Big Losses with Reason Codes for Stop Times to create a balanced perspective on where the team should prioritize their time.
Total Parts
Total Parts is the total of all produced parts (including Defects). The quantity of Total Parts is referred to as Total Count and is used to calculate OEE Performance and OEE Quality.
Unplanned Stop
Unplanned Stop means the manufacturing process is scheduled for production and is not running because of an event like an equipment failure or material shortage. Unplanned Stops affect OEE Availability.
Utilization
Utilization is the percentage of calendar time that is used for production. Utilization is an important part of TEEP. Utilization takes into account the losses of Production Not Scheduled, and Plant Not Open.
Visual Factory
Visual Factory is a concept for reducing communication waste on the factory floor through the use of real time indicators such as signs, charts, and scoreboards. Andon indicators are often an important tool in the visual factory.
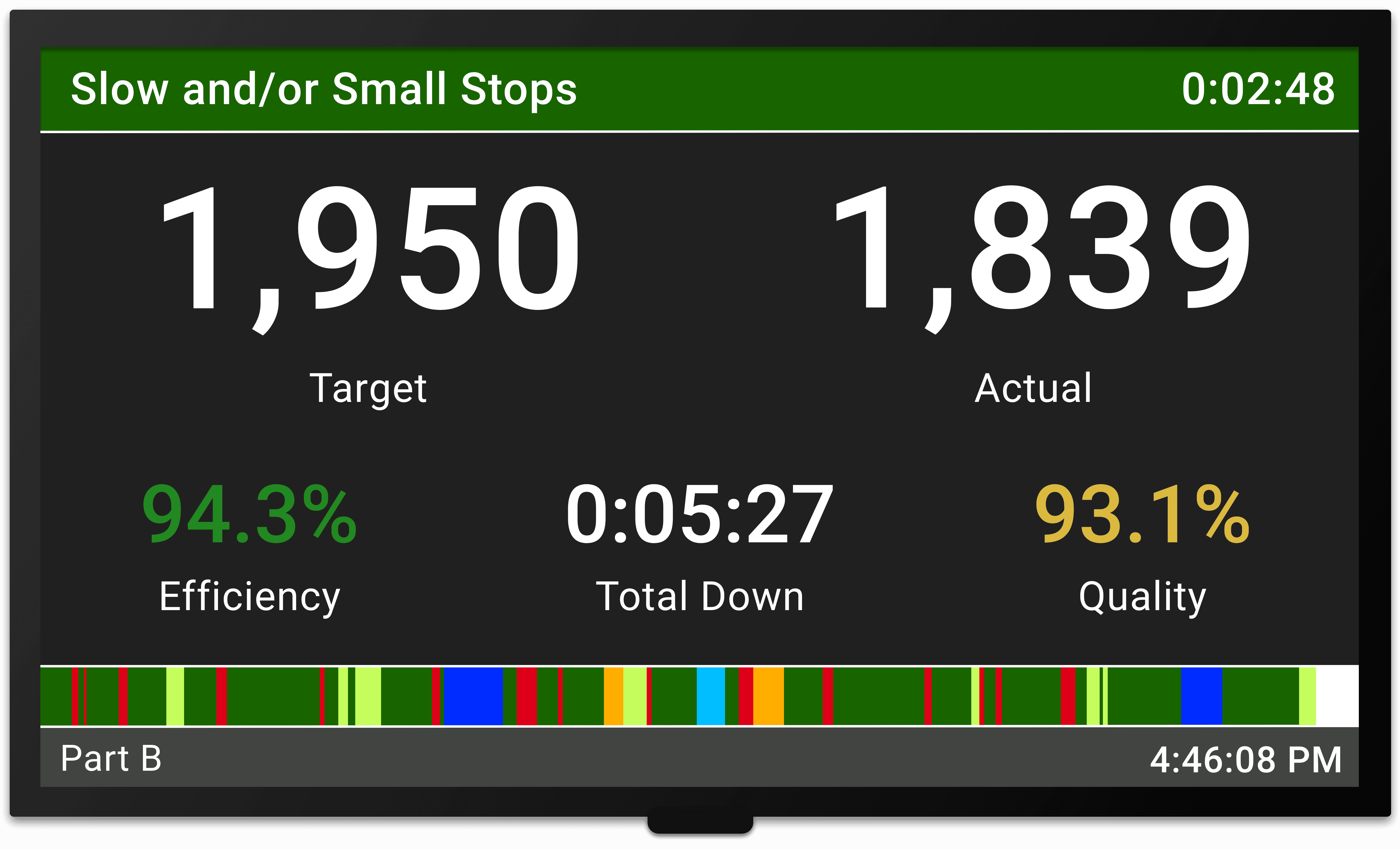
Visual OEE™
Visual OEE™ is a plant floor real-time display of live OEE data for maximum team involvement. Visual OEE™ displays make improvement everyone’s job.
WIP
WIP stands for “Work in process” and represents any semi-manufactured part that is not ready for sale to the customer.
World Class OEE
World Class OEE is a term that is often used to refer to an OEE score of 85%, with a breakdown to the following OEE Factors:
- 90% Availability
- 95% Performance
- 99% Quality
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO NEXT...
1. Learn more about how our product, Vorne XL, can help you eliminate waste and significantly improve OEE.
Vorne XL is the simplest and fastest way to monitor and improve production. It's a one-time cost and takes just a day to install. And you can try it completely free for 90 days.
Learn More2. Download our FREE package of tools to supercharge your manufacturing productivity
The package includes leadership lessons, training guides, meeting and report templates, summaries of key concepts, project organizers, and more. You'll also receive our monthly newsletter for free. Unsubscribe at any time.
DOWNLOAD FREE LEAN TOOLS3. Sign up for our monthly newsletter
Get free monthly updates with proven methods for improving our manufacturing productivity. Unsubscribe at any time.